How third-party commissioning agents can improve building construction.
Over the last three decades, I worked with thousands of buildings and witnessed firsthand a critical issue in the building industry: Construction Quality. Serious building deficiencies are shockingly common.
These flaws are born from a construction event — not only in new construction but remodels and simple equipment replacements as well. The prevalence of quality deficiency in all building types: big and small, simple and complex, commercial and residential; is on the rise. Retail, restaurant, office, grocery, lodging, education, warehouse, data center, healthcare… none are immune.
As a result, we have buildings with:
- Unhealthy and uncomfortable indoor environments
- High energy use
- Soaring repair and maintenance costs
Causes of Poor Construction Quality
I observed four key root causes of poor construction quality:
- Pressure on time and money – As a society, we want things faster and cheaper, and buildings are no exception. This constricts construction teams, forcing errors and cut corners. Important design elements are ignored or intentionally removed from scopes of work.
- Scarcity of skilled labor – The skilled labor shortage is a national challenge and is worsening. Because of this, people are installing building systems without proper training and experience. Even when intentions are good, mistakes happen.
- Lack of integrity – Sadly, personal character and ethics are undervalued by many. Frequently I see contractor reports claiming certain tasks were complete but, upon inspection, were found incomplete… A construction checklist indicating the presence of important equipment accessories that are missing, a balance report showing airflow set to design while the necessary components are not installed, the list goes on. Much of the construction process is invisible to building owners and thus ripe for dishonesty.
- Absence of accountability – The vast majority of construction issues are being overlooked. When they are caught, they are not being pursued to a successful resolution. This problem is exacerbated for chain building owners trying to manage dozens, if not hundreds, of projects at once. They are unable to keep up, and their level of oversight diminishes.
Commissioning: How to Improve Construction Quality
So, what can be done? Give construction contractors more time and money to do their job and, though that may help, that doesn’t ensure success. The skilled labor shortage is a long-term problem and will not be solved any time soon. We can and should associate with those who have integrity, but we must verify that our trust in them is justified.
What can we do immediately? We can improve construction quality, provide accountability by auditing, and inspect the construction process. In other words, we can commission the building.

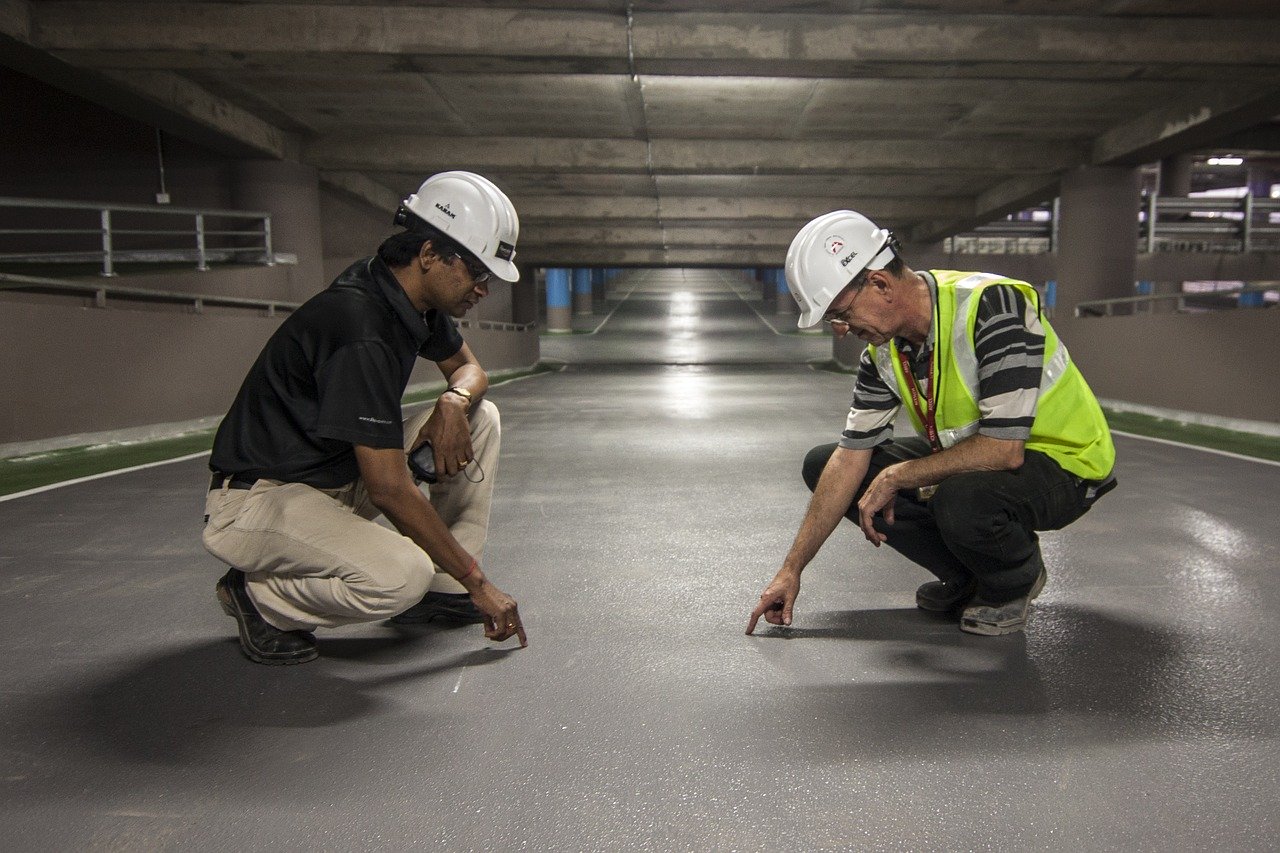
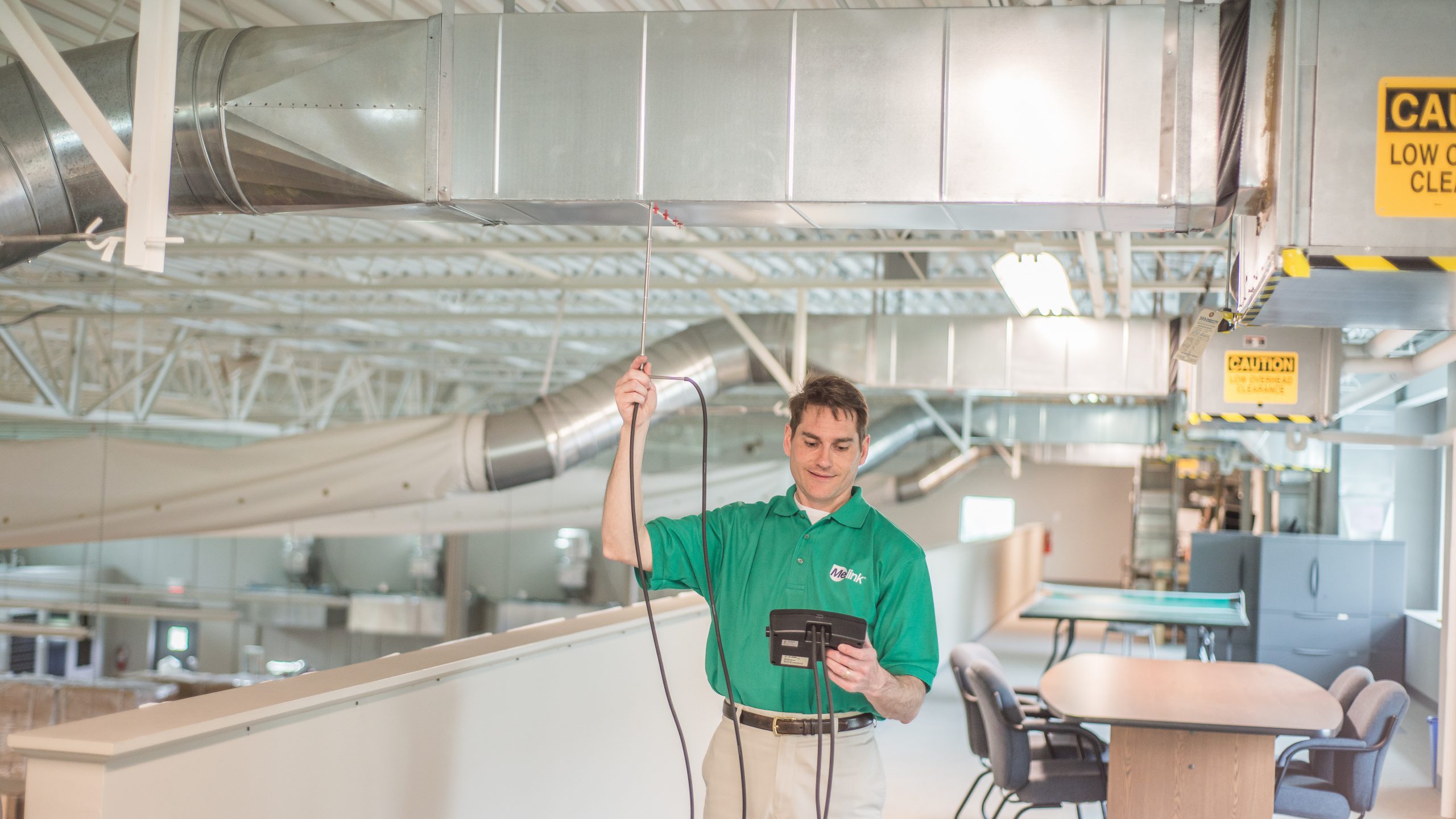
Independent commissioning agents work alongside the design and construction teams, objectively checking things along the way. However, they do not replace those teams or their responsibilities. The commissioning agents examine particular details of the building systems and determine how those systems work together. Experienced and diligent commissioning agents uncover construction deficiencies and work with the appropriate contractors to appropriately resolve issues.
Without accountability built into our construction processes, (AKA commissioning) the quality of buildings will only continue to worsen.
Melink offers commissioning services. Contact us to learn more.